✔ Competitive Pricing ✔ Quality Service ✔ Extensive Stock ✔ Experienced Staff
 Price
PriceBasic Guide to Woodturning for Beginners
A Beginners Guide to Woodturning
A quick summary of things you need to know before woodturning for the first time.
Essential Woodturning Equipment
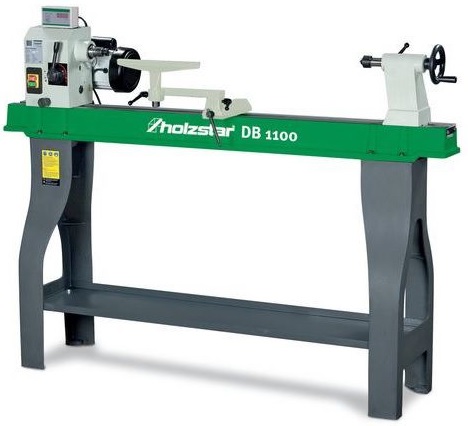 * Lathe: Spins the wood for shaping. Find lathes here.
* Lathe: Spins the wood for shaping. Find lathes here.
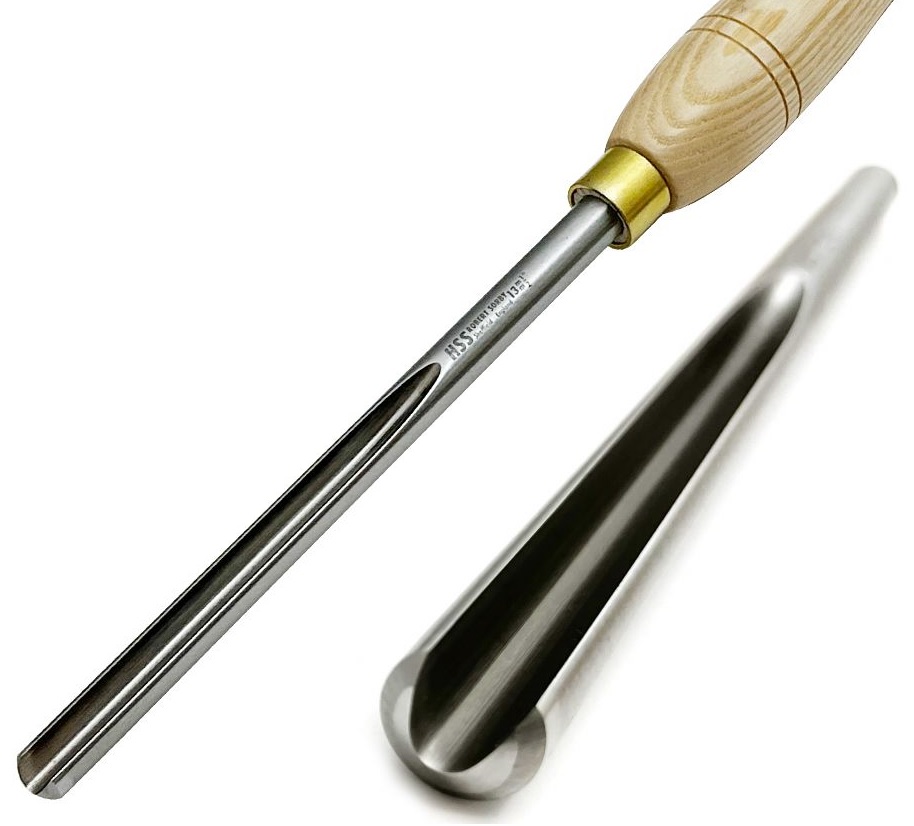 * Bowl Gouge: For hollowing and shaping bowls. Comes in various grinds (e.g., fingernail, swept-back) for roughing and finishing. Find bowl gouges here.
* Bowl Gouge: For hollowing and shaping bowls. Comes in various grinds (e.g., fingernail, swept-back) for roughing and finishing. Find bowl gouges here.
 * Spindle Gouge: Use when turning between centres (e.g. turning pens, legs). Ideal for shaping curves, beads, and coves. Find spindle gouges here.
* Spindle Gouge: Use when turning between centres (e.g. turning pens, legs). Ideal for shaping curves, beads, and coves. Find spindle gouges here.
 * Roughing Gouge: Removes bulk material quickly. Not suitable for bowl turning due to its wide flute and potential for catches. Find roughing gouges here.
* Roughing Gouge: Removes bulk material quickly. Not suitable for bowl turning due to its wide flute and potential for catches. Find roughing gouges here.
 * Skew Chisel: Creates smooth finishes and fine details. Can be tricky to master but delivers crisp cuts and elegant finishes. Find skew chisels here.
* Skew Chisel: Creates smooth finishes and fine details. Can be tricky to master but delivers crisp cuts and elegant finishes. Find skew chisels here.
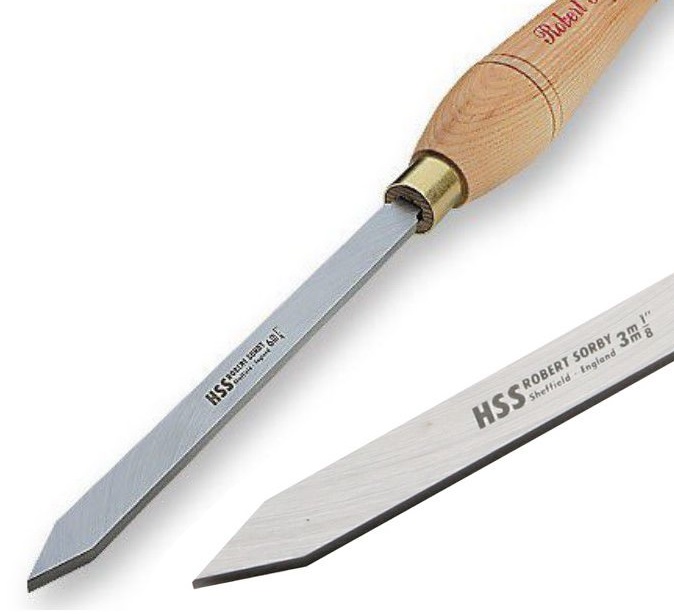 * Parting Tool: Cuts grooves and separates pieces. Find parting tools here.
* Parting Tool: Cuts grooves and separates pieces. Find parting tools here.
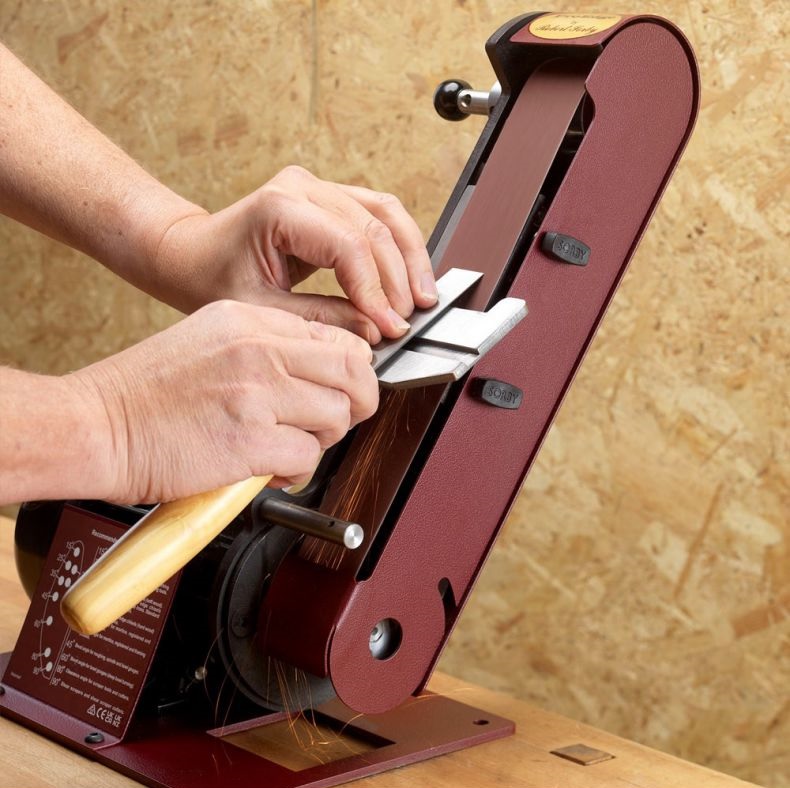 * Sharpening System: Keeps tools razor-sharp. Find sharpening systems here.
* Sharpening System: Keeps tools razor-sharp. Find sharpening systems here.
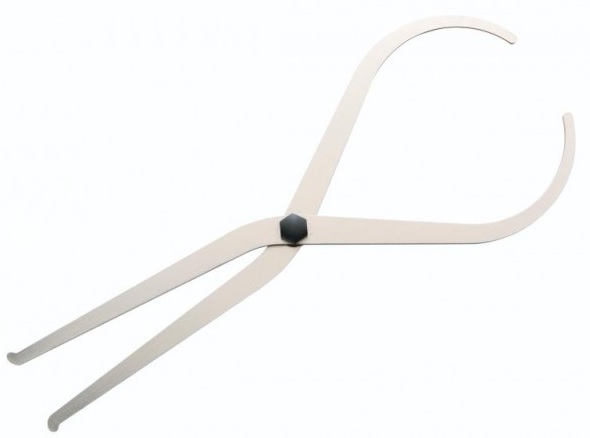 * Callipers: Measures thickness and diameter. Helps maintain symmetry and precision. Find callipers here.
* Callipers: Measures thickness and diameter. Helps maintain symmetry and precision. Find callipers here.
Types of Woodturning
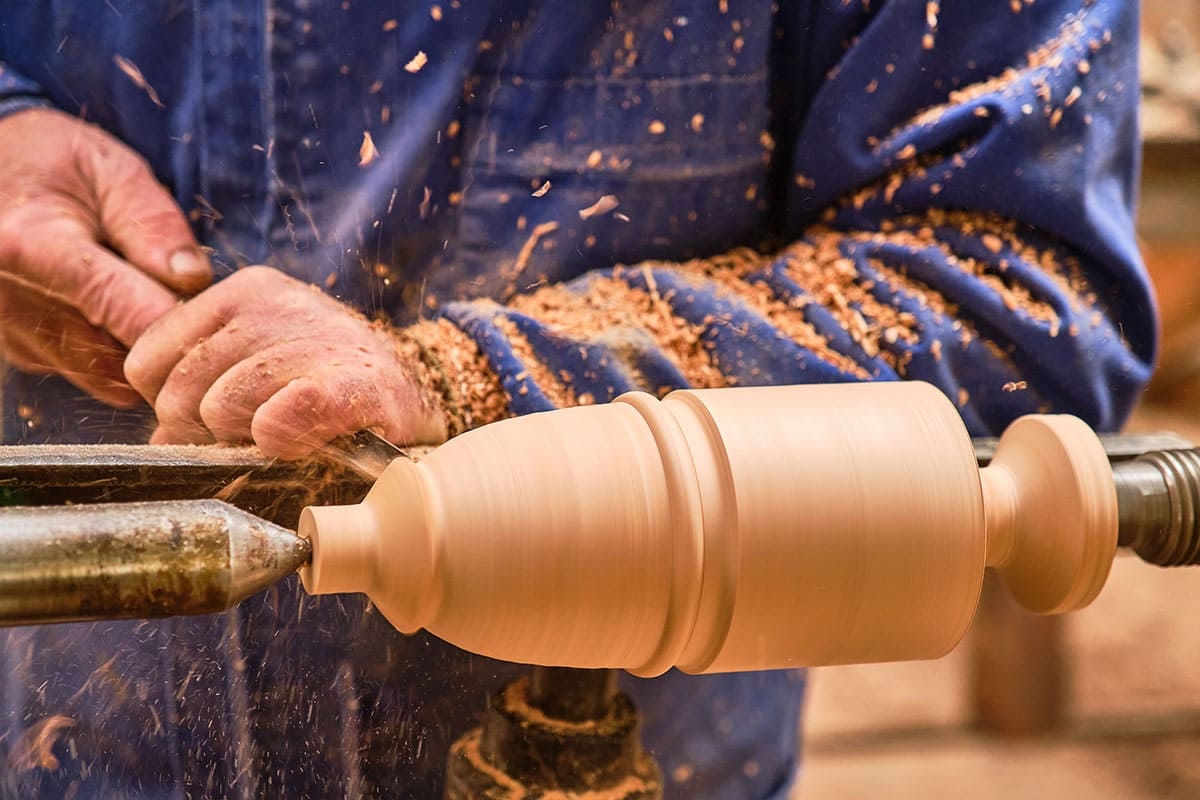
Spindle Turning
Spindle turning is a foundational woodturning technique where the wood is mounted between the headstock and tailstock of a lathe and rotated along its long axis. This setup allows you to shape long, narrow pieces such as chair legs, table spindles, candlesticks, tool handles, and baseball bats. It’s great for beginners as it eaches tool control and precision, it's easier to manage than bowl turning due to consistent grain direction, and it builds muscle memory for shaping and detailing.

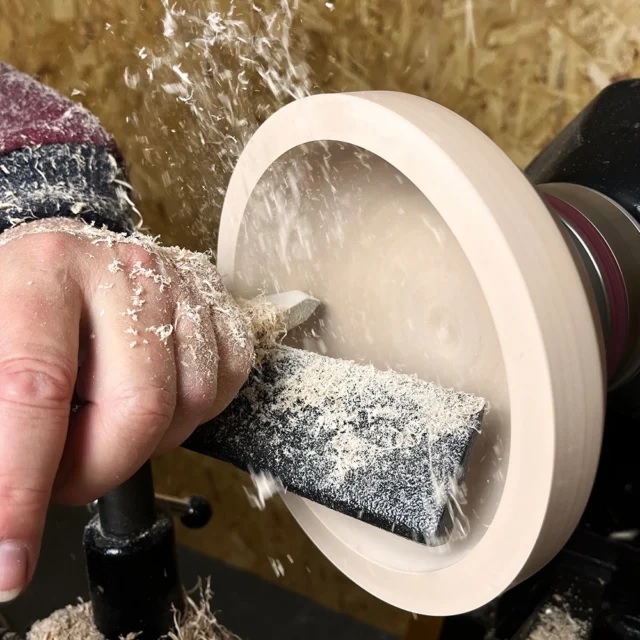
Faceplate Turning
Faceplate turning is a woodturning technique where the workpiece is mounted to a faceplate, which is a flat, circular metal disc attached to the lathe’s spindle. Unlike spindle turning (where the grain runs parallel to the lathe bed), faceplate turning involves side-grain orientation, meaning the grain runs perpendicular to the lathe bed. This setup is ideal for turning wide, flat objects.

Safety Precautions
It's important to stay safe while woodturning, not only are you dealing with the risks that come with operating machinery, you are also contending with dust and noise. When woodturning you should avoid distractions. If you're tired, stressed, or under the influence, postpone your turning session. It's also important to know your limits, don’t push beyond your skill level, especially with complex cuts or large blanks.





 01726 828 388
01726 828 388






